Iranian Pistachio Varieties, A Comprehensive Guide
Iranian Pistachio Varieties, Pistachio is one of the most important types of nuts in Iran and the world. The pistachio tree probably originated in Central or East Asia and has different species. The types of pistachios cultivated in Iran belong to the domestic species with the scientific name of Pistacia Vera. Pistachio trees are dicotyledonous in the sense that male and female flowers are produced on different trees and on one tree there are no both male and female flowers.

Iranian Pistachio Varieties
Here, we try to mention the characteristics of famous pistachio cultivars in the world with a focus on two important producing countries, namely Iran and the United States, and also explain a summary of the characteristics of other types of pistachios in other countries producing this product.
Important pistachio producer countries
Iran, the United States, Turkey, China, Syria, Greece, Italy, Afghanistan, Tunisia and Spain are the top 10 pistachio producing countries in the world. Due to the fact that the United States has a high domestic consumption, Iran is considered as the largest exporter of pistachios. Other pistachio producing countries include Madagascar, Australia, Kyrgyzstan, Jordan, Uzbekistan, Pakistan, Ivory Coast, Morocco and Mexico.
Iranian Pistachio Varieties
Iran has more than 70 cultivars and genotypes of female pistachios and a large number of male genotypes and is one of the most important sources of pistachio germplasm in the world. The most famous types of pistachios in Iran are: Koleghoochi, Akbari, Mumtaz, Badami Zarand, Sefid pistachio Nogh, Ahmad Aghaei, Ouhadi, Khanjari Damghan, Shah Pasand Damghan and Qazvini pistachio.
There are different divisions for different types of Iranian pistachios. In a general division, pistachio types are grouped into two categories: Fandoghi and Almond . For example, Kalleghuchi and Ouhadi cultivars are classified in the Fandoghi group and Akbari, Ahmad Aghaei, Mumtaz and Sefid Pistachio cultivars are classified in the almond group.
In another classification, pistachios are classified into three groups in terms of flowering time: early flowering, medium flowering and late flowering. For example, white pistachio cultivars Noghi and Kalleghuchi are grouped in Zodgol group, Ouhadi, Ahmad Aghaei and Badami Zarand cultivars are grouped in medium flower group and Qazvini and Akbari cultivars are grouped in Dir Gol group.
In the third division, pistachio types are grouped into 5 groups in terms of time of product ripening: very early, early, medium clay, late ripening and very late ripening. For example, very early Qazvini cultivar in very early group, Ouhadi and Qazvini early cultivars in early group, Koleghoochi, Khanjari and Shahpasand cultivars of Damghan and Badami in medium clay group, Ahmad Aghaei and Akbari cultivars in late group and Ebrahimi and Jandaghi cultivars in group They are too late. Very early cultivars can be harvested until 31 August, early cultivars from 1 to 10 September, medium cultivars from 11 to 20 September, late cultivars from 21 to 31 September and very late cultivars from 1 to 10 October.
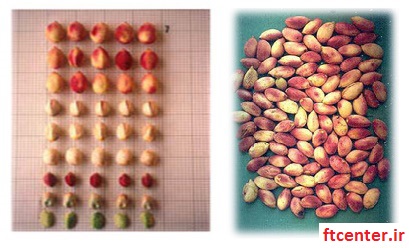
Characteristics of the most famous pistachio cultivars in Iran
Monotonous or Fandoghi
The shape of the fruit is spherical (Fandoghi), the percentage of laughter is very high, the surface color of the purple kernel and the color of the bone skin of the cream.

Iranian Pistachio Varieties
Kalle Ghuchi
hazelnut fruit shape, medium smile percentage, red-gray core color and bone-white skin color with medium opacity.

Iranian Pistachio Varieties
Ahmad Aghaei
The shape of an elongated rectangular fruit (almond), a high percentage of laughter, the color of the purple core and the color of the bone skin are very light.

Iranian Pistachio Varieties
Akbari
The shape of the almond fruit has a high percentage of laughter, the surface color of the kernel is purple-brown and the bone skin color is dark cream.

Iranian Pistachio Varieties
Unfortunately, there are no specific cultivars of the male tree in Iran, and males are usually classified in terms of early flowering, medium flowering, and late flowering. In Iranian gardens, the ratio of the number of male trees to the number of female trees is about 1 to 15 to 1 to 25.
Selection of pistachio base in pistachio cultivation
In pistachio cultivation, the choice of rootstock as the root system of the plant is very important.
In Iran, three bases of P. vera (domestic pistachio), P. khinjuk (Chatlanqush) and P. mutica (pistachio) are used for pistachio cultivation . The use of 2 stems of pistachio and chrysanthemum in Iranian pistachio orchards is very rare and in more than 99% of the country’s pistachio orchards, domestic pistachio rootstock is used. The base of domestic pistachio cultivated in Iran is usually Zarand almond. After planting the base and reaching the age of transplanting, the famous cultivars are transplanted on it. One of the important characteristics of coriander rootstock is resistance to nematode producing pistachio root gland. It is said that the base of Chatlanqush has good resistance to drought.
In other countries of the world, the bases of P. terebintus , P. atlantica , P. integerrima , UCBI, PGI and PGII are used. The three bases UCBI, PGI, and PGII are the result of breeding programs and the cross between P. atlantica and P. integerrima .
P. atlantica rootstock is one of the most commonly used rootstocks in California due to its high resistance to cold. The problem with this base is susceptibility to Verticillium wilt disease. Recently, the use of P. integerrima rootstock has been strengthened in breeding programs due to its resistance to Verticillium wilt disease.
A review of the types of pistachios grown in the United States
About 97% of the pistachios grown in the United States are from a female cultivar called Kerman and a male cultivar called Peters. Kerman pistachio cultivar was taken to California by seeds from Rafsanjan in 1929, and after several years, this cultivar was widely cultivated in the United States.
Characteristics of Kerman cultivar: medium growth strength, direct growth, flower production in late March and early April, uniform maturation on the tree, late (fruit production from September to mid-October) and high cooling requirements. The growth rate of Kerman cultivar and P. integerrima rootstock is similar.
Characteristics of Kerman pistachio fruit: round fruit, crisp and suitable kernel, pink and greenish yellow. High percentage of laughter and of course in some years has a high percentage of emptiness.

Iranian Pistachio Varieties
The figure of Peters
was introduced by Mr. Peters, which probably originated in Armenia. This cultivar produces suitable pollen grains and with about 3 weeks flowering period, has a good overlap with Kerman female cultivar for pollination of this cultivar. Other male cultivars include “Kaz”, “Ell”, “Chico” and “Randy”, which may have originated in Azerbaijan.
Other pistachio cultivars grown in California
Red Aleppo
One of the first varieties cultivated in California, it has an annual, early ripening, has smaller and drier fruits compared to Kerman, and has hanging branches.
“Joley” variety
The product of American breeding programs, some features compared to Kerman cultivar are earlier flowering (one week), earlier (one week), percentage of laughter similar to Kerman, with annuals similar to Kerman.
Others less common varieties

Iranian Pistachio Varieties
Some other cultivars grown in California are imported from the Mediterranean and West Asian countries and are:
Ibrahim (EbrahimAbadi), Ohadi, Safeed, Shasti, Wahedi, Bronte, Buenzle, Lassen, Minassian, SfaxandTrabonella.
Some types of pistachios in California belong to other countries and seem to taste better than the Kerman variety (especially small fruit cultivars from Italy).
Golden Hill and Lost Hill cultivars have been obtained from breeding programs in the United States and may replace the Kerman cultivar in the future. These cultivars are earlier and have a higher laugh rate and have less infection problems than Kerman cultivar.

Iranian Pistachio Varieties
Randy male cultivar
The first flowering occurs 10 to 15 days before Peters, its flowering period overlaps with Kalleghuchi cultivar as well as Golden Hill and Lost Hill cultivars.

Iranian Pistachio Varieties
The most famous types of pistachios in other countries
The most important cultivars cultivatedin other countries are as below:
Syria : “Ashouri”, “Red Oleimy”, “White Batouri”.
Turkey : “Uzun”, “Kirmizi”, “Halebi”, “Abiad miwahi”, “The Jalale”, “Aintaby” and “Ayimi”.
Turkestan (Central Asian region): Kouchka, Akart-Tachecme and Chor-Tchechime
Greece : Larnaca, Aegina and Pontikis.
Spain : “Kerman”, “Aegina”, “Mateur” and “Larnaca”.
Italy : “Bianca” or synonymous with “Napoletana”.
Australia : “Sirora”.
Characteristics of famous pistachio cultivars in other countries
“Ashouri” cultivar known as “Red Aleppo”: green skin color, medium-sized fruit, with a light brown hull with black spots, good quality, cultivated in Syria.
Iranian Pistachio Varieties
“Uzun” cultivar: medium fruit size, elongated and smooth skin, cultivated in Turkey.
Kirmizi cultivar: medium fruit size, red skin color. This cultivar along with “Uzun” cultivar are among the most famous cultivars in Turkey.

Iranian Pistachio Varieties
Kouchka cultivar: thick fruit, creamy white skin color and good fruit quality.
“Mateur” cultivar: elongated fruit, medium size, greenish-yellow skin color, good fruit quality, was selected from Tunisia and showed good results in Spain.
Larnaka cultivar: Medium fruit size, less elongated than “Mateur” fruit. Its origin is Cyprus. Cultivation of this cultivar in Greece and Spain has shown good results.
Aegina cultivar: Medium-sized, elongated fruit, similar to Mateur. Originally from Greece and showed good results in Spain.
Cultivar “Bianca” or its synonym “Napoletana”: small to medium fruit size, elongated fruit shape, dark green fruit color, which is widely cultivated in Italy.
“Sirora” cultivar: has a red skin color, derived from the breed of “Red Aleppo” cultivar and has a green fruit kernel, good quality and high yield, and is cultivated in Australia.
Ferdowsi Trading Center is the first university based trading company in Iran, providing you with best quality pistachios directly from farms of Khorasan province, Iran. You are welcomed to check our pistachio page and contact us in case you had an inquiry.
 لینک کوتاه این صفحه: ftce.ir/ke43b
لینک کوتاه این صفحه: ftce.ir/ke43b













Leave a Reply